Legal Basis
Statutory Powers
The Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe (RBZ) derives its powers to oversee, supervise and operate payment systems primarily from the Reserve Bank Act (Chapter 22:15), and the National Payment Systems Act Chapter 24:23 (NPS Act) :
Read in conjunction with the following statutes:
- Banking Act (Chapter 24:20),
- Bills of Exchange Act [Chapter 14:02] and
- Bank Use Promotion and the Suppression of Money Laundering Act [Chapter 24:24].
- Exchange Control Act [Chapter 22:05]
The NPS Act empowers the Reserve Bank to adequately monitor and regulate the payment system activities in order to ensure compliance and financial stability.In addition, the Central Bank is also guided by international best practices and standards.
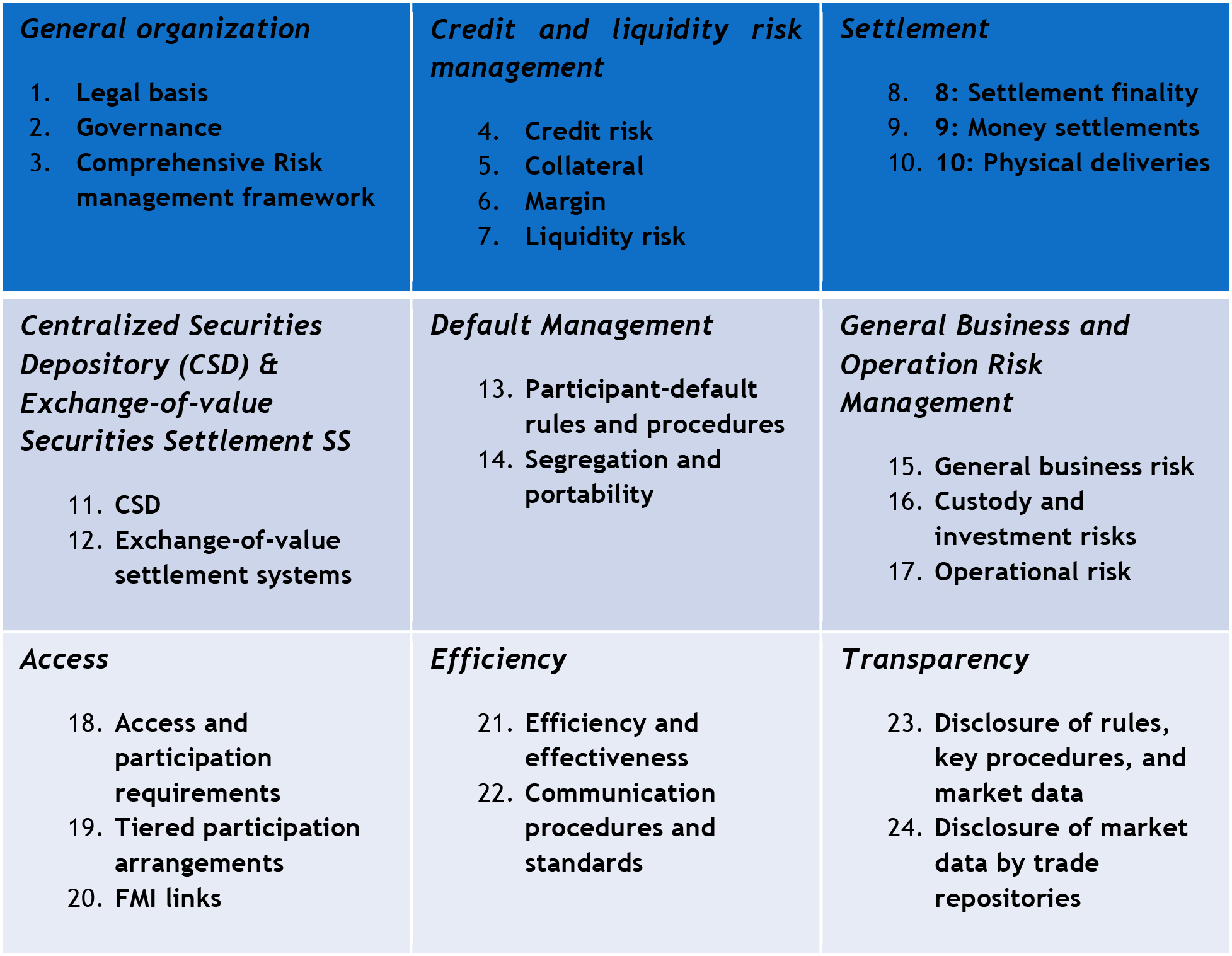
The Central Bank subscribes and adopted (2013) the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Committee on Payment and Market Infrastructures (CPMIs) 24 Principles for Financial Market Infrastructures (PFMIs) and five (5) Central bank responsibilities.
These principles were issued in April 2012, by the BIS CPMIs in collaboration with the International Organization for the Securities Commission (IOSCO) to replace the old sets of international standards set out in the; Core principles for systemically important payment systems (CPMIs, 2001) Recommendations for securities settlement systems (CPMIs-IOSCO, 2001) Recommendations for central counterparties (CPMIs-IOSCO, 2004).
The PFMIs provide a single set of standards that caters for different risks inherent in various payment, clearing and securities settlement systems as summarised below:
Five Central Bank Responsibilities
A: Regulate, supervise, and oversee FMIs
B: Have powers and resources to regulate, supervise, and oversee
C: Disclose Oversight policies with respect to FMIs
D: Apply PFMIs
E: Cooperate with other authorities
24 Principles for Financial Markets Infrastructures (PFMIs)